分布式深度学习平台整理
分布式深度学习平台整理
本文主要收集了如下支持分布式的深度学习平台
- mxnet
- CNTK
- Distributed TensorFlow
- Caffe On Spark
- Torch DistLearn
- Elephas
mxnet
MXNet is a deep learning framework designed for both efficiency and flexibility. It allows you to mix the flavours of symbolic programming and imperative programming to maximize efficiency and productivity. In its core, a dynamic dependency scheduler that automatically parallelizes both symbolic and imperative operations on the fly. A graph optimization layer on top of that makes symbolic execution fast and memory efficient. The library is portable and lightweight, and it scales to multiple GPUs and multiple machines.
MXNet is also more than a deep learning project. It is also a collection of blue prints and guidelines for building deep learning system, and interesting insights of DL systems for hackers.
Features
- Design notes providing useful insights that can re-used by other DL projects
- Flexible configuration for arbitrary computation graph
- Mix and match good flavours of programming to maximize flexibility and efficiency
- Lightweight, memory efficient and portable to smart devices
- Scales up to multi GPUs and distributed setting with auto parallelism
- Support for python, R, C++ and Julia
- Cloud-friendly and directly compatible with S3, HDFS, and Azure
CNTK
https://github.com/Microsoft/CNTK
CNTK (http://www.cntk.ai/), the Computational Network Toolkit by Microsoft Research, is a unified deep-learning toolkit that describes neural networks as a series of computational steps via a directed graph. In this directed graph, leaf nodes represent input values or network parameters, while other nodes represent matrix operations upon their inputs. CNTK allows to easily realize and combine popular model types such as feed-forward DNNs, convolutional nets (CNNs), and recurrent networks (RNNs/LSTMs). It implements stochastic gradient descent (SGD, error backpropagation) learning with automatic differentiation and parallelization across multiple GPUs and servers. CNTK has been available under an open-source license since April 2015. It is our hope that the community will take advantage of CNTK to share ideas more quickly through the exchange of open source working code.
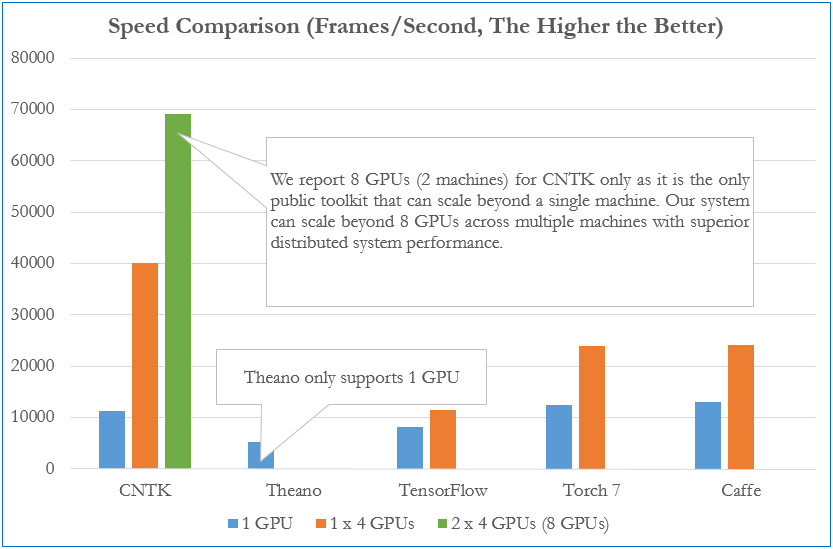
Speed Comparison
Distributed TensorFlow
https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/tree/master/tensorflow/core/distributed_runtime
TensorFlow is an open source software library for numerical computation using data flow graphs. Nodes in the graph represent mathematical operations, while the graph edges represent the multidimensional data arrays (tensors) that flow between them. This flexible architecture lets you deploy computation to one or more CPUs or GPUs in a desktop, server, or mobile device without rewriting code. TensorFlow also includes TensorBoard, a data visualization toolkit.
Distributed TensorFlow is an open-source implementation of the distributed TensorFlow runtime, using gRPC for inter-process communication.
Caffe On Spark
https://github.com/yahoo/CaffeOnSpark
CaffeOnSpark brings deep learning to Hadoop and Spark clusters. By combining salient features from deep learning framework Caffe and big-data frameworks Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop, CaffeOnSpark enables distributed deep learning on a cluster of GPU and CPU servers.
As a distributed extension of Caffe, CaffeOnSpark supports neural network model training, testing, and feature extraction. Caffe users can now perform distributed learning using their existing LMDB data files and minorly adjusted network configuration.
CaffeOnSpark is a Spark package for deep learning. It is complementary to non-deep learning libraries MLlib and Spark SQL. CaffeOnSpark's Scala API provides Spark applications with an easy mechanism to invoke deep learning (see sample) over distributed datasets.
Features
- It enables model training, test and feature extraction directly on Hadoop datasets stored in HDFS on Hadoop clusters.
- It turns your Hadoop or Spark cluster(s) into a powerful platform for deep learning, without the need to set up a new dedicated cluster for deep learning separately.
- Server-to-server direct communication (Ethernet or InfiniBand) achieves faster learning and eliminates scalability bottleneck.
- Caffe users' existing datasets (e.g. LMDB) and configurations could be applied for distributed learning without any conversion needed.
- High-level API empowers Spark applications to easily conduct deep learning.
- Incremental learning is supported to leverage previously trained models or snapshots.
- Additional data formats and network interfaces could be easily added.
- It can be easily deployed on public cloud (ex. AWS EC2) or a private cloud.
Torch DistLearn
https://github.com/twitter/torch-distlearn
Some common distributed learning algorithms built in Torch with the help of the the ipc library.
- AllReduceSGD
Spreads the computation of gradients for mini-batch of items across N processes. Uses AllReduce to quickly sum the gradients and distribute the total back out to every process. - AllReduceEA
We also have a AllReduce based implementation of the Elastic Averaging algorithm as described in Deep learning with Elastic Averaging SGD. Its just as easy to add this to your training script, there are only two parameters required tau and alpha. Tau is how many steps to run before averaging the nodes and alpha is the weight used during the averaging step. You can read more about our implementation of AllReduceEA.
Elephas
https://github.com/maxpumperla/elephas/
Elephas is an extension of Keras, which allows you to run distributed deep learning models at scale with Spark.
Elephas currently supports a number of applications, including:
- Data-parallel training of deep learning models
- Distributed hyper-parameter optimization
- Distributed training of ensemble models
Schematically, elephas works as follows.

A simple comparison
https://github.com/zer0n/deepframeworks