Data Curation
Data Curation at Scale: The Data Tamer System
Data Curation常被译为数据保管、数据保存等。业内有很多有关Data Curation的定义,比较有代表性的是英国数字保管中心(Digital Curation Centre,简称DCC)的定义如下。
Data Curation指的是在数字数据的生命周期内,对这些数据进行维护、保存以及实现价值增值的所有活动,这些活动能够提高现有数据的长期利用价值;主动管理这些数据有利于减少在重新研究这些数据时出现的各种威胁以及降低因数字技术的退化而带来的各种风险;同时,Data Curation所进行的一些列活动还能使在可信赖仓储库中所保管的数据能够更为广泛地共享给研究机构,以便支撑未来的研究活动。
Data curation is the act of discovering a data source(s) of interest, cleaning and transforming the new data, semantically integrating it with other local data sources, and deduplicating the resulting composite.
通常,Data Curation可能有人工进行实现,也会借助于机器学习等方法,只在必须的时候加入人工干预。
For example, one web aggregator requires the curation of 80,000 URLs and a second biotech company has the problem of curating 8000 spreadsheets. At this scale, data curation cannot be a manual (human) effort, but must entail machine learning approaches with a human assist only when necessary.
论文介绍了Data Tamer系统的实现,Data Tamer是一种端到端的Data Curation系统。
This paper describes Data Tamer, an end-to-end curation system we have built at M.I.T. Brandeis, and Qatar Computing Research Institute (QCRI).
https://cs.uwaterloo.ca/~ilyas/papers/StonebrakerCIDR2013.pdf
We have run Data Tamer on three real world enterprise curation problems, and it has been shown to lower curation cost by about 90%, relative to the currently deployed production software.
Characteristics
Data Curation的实现主要需要解决如下的4个问题,包括系统的自动扩展性、脏数据的清洗、系统的操作便捷性、系统对数据需要支持增量操作。
- Scalability through automation. The size of the integration problems we are encountering precludes a human-centric solution. Next generation systems will have to move to automated algorithms with human help only when necessary. In addition, advances in machine learning and the application of statistical techniques can be used to make many of the easier decisions automatically.
- Data cleaning. Enterprise data sources are inevitably quite dirty. Attribute data may be incorrect, inaccurate or missing. Again, the scale of future problems requires an automated solution with human help only when necessary.
- Non-programmer orientation. Current Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) systems have scripting languages that are appropriate for professional programmers. The scale of next generation problems requires that less skilled employees be able to perform integration tasks.
- Incremental. New data sources must be integrated incrementally as they are uncovered. There is never a notion of the integration task being finished.
Data Tamer Semantic Model
Human Roles
Data Tamer支持必要的人工干预,其中人的角色按照其功能可分为DTA和DE,DTA相当于传统的数据库管理员,DE是领域专家,主要解决与领域相关的数据管理问题。
A Data Tamer administrator (DTA). This role is analogous to a traditional database administrator.
One or more Domain Experts (DE). These are human domain experts that can be called on to answer questions that arise during the curation process.
Sites and Schemas
针对元数据信息量的多少,可以分为如下的3个层级。Level 1中对数据一无所知,因此可以采取从低至上的策略对数据进行整理;Level 2中对部分数据有一定了解,因此采取了从低至上和从上至下相结合的方法对方法,对已知数据采用相应的模板进行匹配;Level 3中对数据完全掌握,理想状态下只需要采用模板对数据采用至上而下的策略进行匹配即可。实际中,Level 1和Level 3的情况较少出现,主要是Level 2的情况。
Level 3: Complete knowledge. In this case, the complete global schema for a given class of entities has been specified by the DTA using a top-down methodology.
Level 1: No knowledge available. In this case, nothing is known about the structure of the classes of information, and a bottom-up integration is utilized.
Level 2: Partial information available. Using either a top-down or bottom-up methodology, there may be partial information available. There may be specific attributes that are known to be present for some class of entities. Alternately, there may be templates available. A template is a collection of attributes that are likely to appear together in one of more classes of entities.
Other Information
在不少领域,除了数据本身所携带的信息,还存在不少可供使用的字典类外部数据。Data Tamer同样使用了该类数据。
In addition, in many domains, there are standard dictionaries, which should be used by Data Tamer. A dictionary is a list of data values of some data type that can populate an attribute in some data source.
Management Console and Data Tamer Actions
站点、类别、模板、字典、表、别名等都可由数据管理员通过界面进行配置。
Sites, categories, templates, dictionaries, authoritative tables, and synonyms can be specified through a DTA management console, which is a fairly traditional-looking GUI.
数据管理员还能配置和数据相关的操作,例如数据的读取,类型标注,实体合并等。
A portion of this console is dedicated to allowing the DTA to specify actions for Data Tamer to take. These actions are:
- Ingest a new data source, and store the incoming data in a Postgres database.
- Perform attribute identification on data source-i.
- Perform entity consolidation on data source-i.
类型标注和实体合并由于牵扯到领域知识,也需要领域专家的参与。
At any time during attribute identification or entity consolidation, Data Tamer may request human assistance from a DE.
类型标注和实体合并也能够进行重新配置。
At any time, the DTA may request that attribute identification and/or entity consolidation be redone on all sites.
Data Tamer保存了所有操作的历史作为快照,支持回滚。
Lastly, Data Tamer keeps a history of all operations performed, and the DTA may "snap" the curation process backwards to any past historical point.
Training Data
在实际使用过程中,对数据的相关知识主要包括两个来源,即预先定义的规则和使用过程中积累下来的知识。
The first one is appropriate for cases with minimal or no advance knowledge (i.e., levels 1 and 2 above). As such, training data is simply accumulated over time by the crowd-sourcing component of Data Tamer.
The second scenario deals with applications where more information is known (level 3 above). Therefore, they provide hand-curated collections of known matches.
In the first scenario we start running the Data Tamer system, asking a human for help as appropriate. In the second scenario, we make use of known duplicates as initial training data.
Data Source Update
Data Tamer知识数据源的更新。
Finally, some data sources may be dynamic, and be continually updated. In this case, Data Tamer can make a new snapshot of a previous data source-k.
Data Tamer Components
Data Tamer的系统框图如下,主要包含了schema integration,entity consolidation,data visualization,以及人工(众包)干预模块。
A block diagram of Data Tamer is shown in Figure 1. Indicated in the diagram are the management console and components for schema integration, entity consolidation, DE support and human transformation. These four subsystems are described in this section. Most of the features described in this section are currently operational.
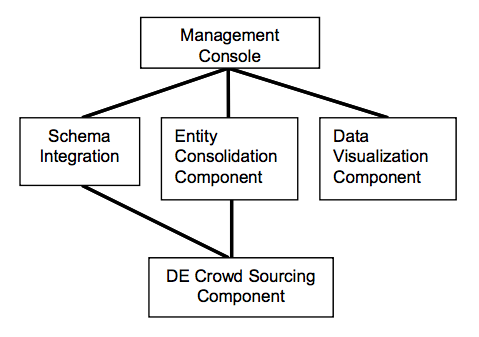
Schema Integration
Schema Integration可以理解成元数据集成,即对从多个数据源获取的数据定义进行集成(例如不同来源的同类数据可能具有不同的定义,需要借助领域专家进行类型标注从而实现统一)。
The basic inner loop in schema integration is to ingest an attribute, Ai from a data source and compare it to a collection of other attributes in a pairwise fashion.
Our approach is to use a collection of algorithms, which we term experts, each returning a score between 0 and 1. Afterwards, the scores are consolidated with a set of weights to produce a composite value.
The attribute mappings to be considered by Data Tamer depend on what information is available for the curation problem at hand,
Entity Consolidation
Entity Consolidation是指多个数据源针对相同的实体可能有不同的定义,因此需要进行统一(或去重)。
Entity consolidation is effectively modeled as duplicate elimination. The goal is to find entities that are similar enough to be considered duplicates. This module receives a collection of records, R1, ..., Rn, from one or more local data sources that arrive incrementally.
具体步骤如下。
- Bootstrapping the Training Process
Initially, the system starts with zero knowledge about the deduplication rules. We learn deduplication rules from a training set of known duplicates and non-duplicates. - Categorization of Records
Records are classified into multiple categories such that each category represents a set of homogenous entities that have similar non-null attributes and similar attribute values. - Learning Deduplication Rules
The deduplication rules are divided into two types: (1) cut-off thresholds on attribute similarities, which help pruning a large number of tuple pairs; and (2) probability distributions of attribute similarities for duplicate and non-duplicate tuple pairs. We learn such rules from the collected training data TP and TN. - Similarity Join
We obtain all candidate tuple pairs, where each pair belong to the same category and at least one attribute has a similarity above its learned threshold. Then, we compute the attribute similarities of the candidate pairs and we use these similarities to identify duplicate records according to the classifier learned. - Record Clustering and Consolidation
Once we obtain a list of tuple pairs that are believed to be duplicates, we need to obtain a clustering of tuples such that each cluster represents a distinct real-world entity.
Human Interface
数据属性识别和实体合并阶段,均需要领域专家的参与,因此Data Tamer提供了相应的界面进行操作,主要两种模式,即Manual Mode和Crowd Sourcing Mode。其中,针对Crowd Sourcing Mode获取的标注还需要进行confidence的计算来确定最终结果。
In both the attribute identification phase and the entity consolidation phase, a human DE may be asked by a DTA to provide curation input. In the case of attribute identification, the task is to decide if two attributes are the same thing or not. In the case of entity resolution, the task is to decide if two entities are duplicates or not.
- Manual Mode
If the tasks requiring human intervention are few or if there are only a few DEs, then the DTA can manually assign human tasks to DEs. - Crowd Sourcing Mode
Large-scale data curation may require enlisting additional DEs with lesser expertise to help with the workload. Non-guru DEs can be asked to complete "easier" tasks, or they could be crowdsourced to produce results with higher confidence of correctness than could be assumed of any of them individually.
Visualization Component
Data Tamer还提供一个可视化界面来展示各个数据源的数据,方便直接对其进行洞察。
At any time, the DTA or a DE can call our visualization system and pass a local data source to that system. It displays the data source (or a sample of the source) as a table on the screen. The human can inspect the data source for insight.
相关连接
- https://cs.uwaterloo.ca/~ilyas/papers/StonebrakerCIDR2013.pdf