Knowledge Graph Algorithms
Knowledge Graph Algorithms
Knowledge Graph Algorithms
知识图谱,也称为科学知识图谱,它通过将应用数学、图形学、信息可视化技术、信息科学等学科的理论与方法与计量学引文分析、共现分析等方法结合,用可视化技术描述知识资源及其载体,挖掘、分析、构建、绘制和显示知识及它们之间的相互联系。为学科研究提供切实的、有价值的参考。
知识图谱的构建通常可以粗分为下面4种方法,主要包括人工标注、众包标注、基于规则的方法从半结构化数据中抽取、基于机器学习等方法从非结构化数据中抽取。
- In curated approaches, triples are created manually by a closed group of experts.
- In collaborative approaches, triples are created manually by an open group of volunteers.
- In automated semi-structured approaches, triples are extracted automatically from semi-structured text (e.g., infoboxes in Wikipedia) via hand-crafted rules, learned rules, or regular expressions.
- In automated unstructured approaches, triples are extracted automatically from unstructured text via machine learning and natural language processing techniques.
目前知识图谱的成功案例及算法分类如下。
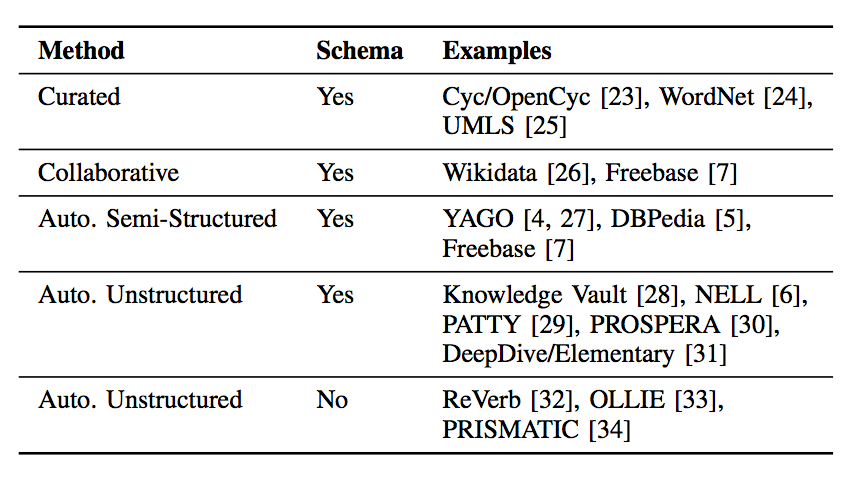
Statistical relational learning for knowledge graphs
知识图谱的实体关系能够表示成为张量的形式,三个维度分别对应了两个实体和关系的类别。
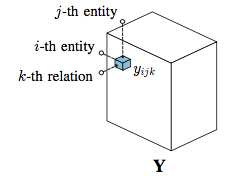
We model each possible triple xijk = (ei,rk,ej) over this set of entities and relations as a binary random variable yijk that indicates its existence.
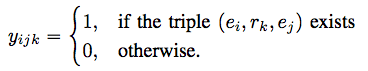
Tensor representation of binary relational data is as follows.
语义角色标注(Semantic Role Labeling)的关键问题是如何在海量稀疏数据中高效的挖掘出可能的关系。
An important issue for SRL on knowledge graphs is how to deal with the large number of possible relationships while efficiently exploiting the sparsity of relationships.
知识图谱通常会包含一些约束,例如类别约束、传递约束,以及一些模式或规则。
Knowledge graphs typically adhere to some deterministic rules, such as type constraints and transitivity and have typically also various "softer" statistical patterns or regularities, which are not universally true but nevertheless have useful predictive power.
这些模式或规则主要包括:同质性、块状结构、全局及长期统计依赖性,其解释如下。
- Homophily: the tendency of entities to be related to other entities with similar characteristics.
- Block structure: entities can be divided into distinct groups (blocks), such that all the members of a group have similar relationships to members of other groups.
- Global and long-range statistical dependencies: dependencies that can span over chains of triples and involve different types of relations.
针对语义角色标注主要包含了下面三种假设,即隐含特征假设、图特征假设、马尔科夫随机场假设,并由此引申出对应的不同模型和算法。
- Assume all yijk are conditionally independent given latent features associated with subject, object and relation type and additional parameters (latent feature models)
- Assume all yijk are conditionally independent given observed graph features and additional parameters (graph feature models)
- Assume all yijk have local interactions (Markov Random Fields)
由第一、二种条件独立性假设可以归纳出如下的概率模型,即基于观测已知量、模型参数、概率假设的整体的似然,其中\sigma是逻辑斯特函数,\Ber是伯努利分布。
The conditional independence assumptions of M1 and M2 allow the probability model to be written as follows:
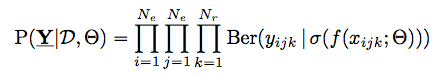
\sigma is the sigmoid (logistic) function,
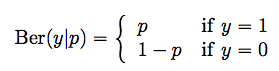
\Ber is the Bernoulli distribution.
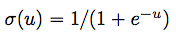
基于概率模型,可以通过某些评价准则进行参数的优化,例如最大化已知关系和未知关系之间的间隔(margin),对应的模型也称为score-based models。
In addition to probabilistic models, f(.) can be optimized under other criteria, for instance models which maximize the margin between existing and non-existing triples, which is refer as score-based models.
Latent Feature Models
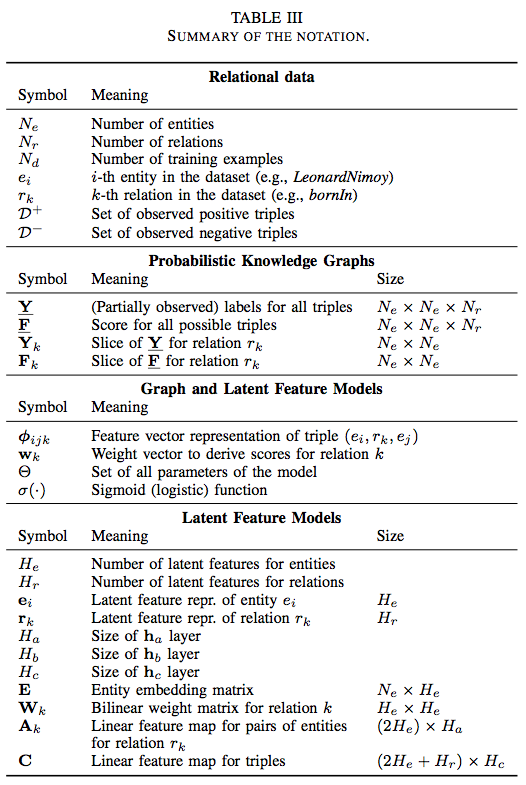
首先介绍基于隐含特征的模型,各个标号的意义可见下表。
RESCAL: A bilinear model
隐含特征模型包含一系列算法,最基本的RESCAL算法是一种双线性模型。
RESCAL算法将关系解释称为隐含特征之间的成对关联。
RESCAL is a relational latent feature model which explains triples via pairwise interactions of latent features. In particular, we model the score of a triple xijk as
RESCAL计算关系\类别的表达式如下,其中e是实体对应的特征向量,w是隐含特征之间关联的权值矩阵。
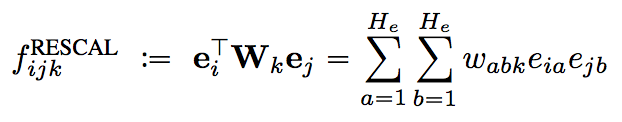
RESCAL之所以称为双线性模型,是因为利用了两实体特征维度的乘积项进行拟合(注意与MLP模型的差别)。
RESCAL is called a bilinear model, since it captures the interactions between the two entity vectors using multiplicative terms.
下面的例子解释了RESCAL算法的工作原理,其主要通过调整权值矩阵优化参数,对数据进行拟合。
For instance, we could model that Alec Guinness is a good actor and that the Academy Award is a prestigious award via the vectors
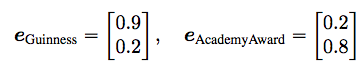
we could model the pattern that good actors are likely to receive prestigious awards via a weight matrix such as
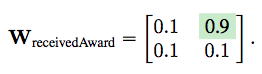
RESCAL的目标函数是最小化对数损失,可以采用梯度算法,例如stochastic gradient descent(类似的优化问题基本都可以采用SGD或ALS,最优化中的基本方法)。
The parameters of RESCAL can be estimated by minimizing the log-loss using gradient-based methods such as stochastic gradient descent.
也可以采用RESCAL-ALS方法,其具有较好的计算复杂度(仅和张量中非零元素的个数成线性关系,由于张量稀疏,因此复杂度较低)。
A single update of E and Wk scales linearly with the number of entities Ne, linearly with the number of relations Nr, and linearly with the number of observed triples, i.e., the number of non-zero entries in Y, it is called algorithm RESCAL-ALS.
Other tensor factorization models
其他张量分解方法,例如CP decomposition(还有Tucker等一系列方法)。
Various other tensor factorization methods have been explored for learning from knowledge graphs and multi-relational data, including factorizing adjacency tensors using the CP tensor decomposition to analyze the link structure of Web pages and Semantic Web data respectively.
Matrix factorization methods
矩阵分解方法,通过将张量的某两维做线性展开成为矩阵,缺点是会丢失展开的两维之间隐含的关联关系。
The adjacency tensor is reshaped into a matrix by associating rows with subject-object pairs and columns with relations, or into a matrix by associating rows with subjects and columns with relation/objects. Unfortunately, both of these formulations lose information compared to tensor factorization.
Multi-layer perceptrons
下面介绍多层感知机模型。
对了和RESCAL模型进行对比,首先将原始RESCAL模型转换成下面的形式。
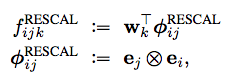
由此可见RESCAL模型拟合的是实体特征之间的乘积项。
Multi-layer perceptrons allows us to consider alternative ways to create composite triple representations and to use nonlinear functions to predict their existence.
MLP模型中常用的是E-MLP模型,其表示如下。
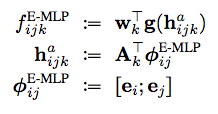
MLP模型的缺点是对某种关系都需要定义不同的权值拟合矩阵,为了解决这个问题可以采用ER-MLP模型(权值拟合矩阵C和关系k独立)。
One disadvantage of the E-MLP is that it has to define a vector wk and a matrix Ak for every possible relation, and ER-MLP is defined as follows, C is independent of the relation k.
ER-MLP模型的表示如下。
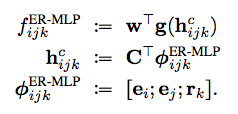
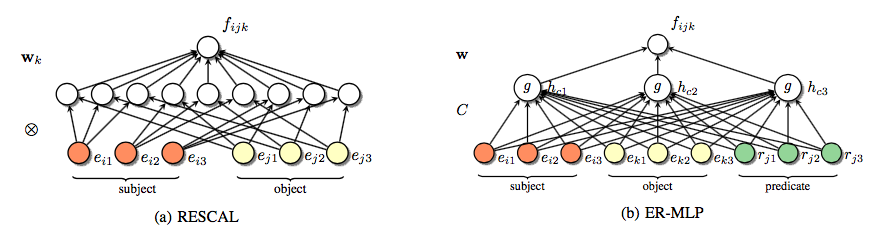
下面对比了RESCAL和ER-MLP对应的神经元网络,可见拟合项存在差异,ER-MLP拟合的是实体特征项的加性项。
Visualization of RESCAL and the ER-MLP model as Neural Networks is as follows. Here, He = Hr = 3 and Ha = 3. Note, that the inputs are latent features.
Neural tensor networks
由于RESCAL和ER-MLP所采用的拟合项不用,容易想到把两个结合起来一起拟合,因此形成了Neural tensor networks模型。
We can combine traditional MLPs with bilinear models, resulting in what calls a "neural tensor network" (NTN). More precisely, we can define the NTN model as follows:
Neural tensor networks的表示如下。
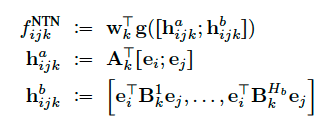
Latent distance models
隐含距离模型通过定义和计算实体向量间估计来拟合实体间关系。
Latent distance models derive the probability of relationships from the distance between latent representations of entities: entities are likely to be in a relationship if their latent representations are close according to some distance measure.
其中主流的是structured embedding/SE模型。
The structured embedding (SE) model extends this idea to multi-relational data by modeling the score of a triple xijk as:
其表达式如下,拟合项为A。
(可以理解成y=kx+b中的k...)
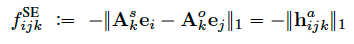
为了减少拟合参数,TransE模型采用了截距进行拟合。
(可以理解成y=kx+b中的b...)
To reduce the number of parameters over the SE model, the TransE model translates the latent feature representations via a relation-specific offset instead of transforming them via matrix multiplications.
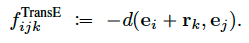
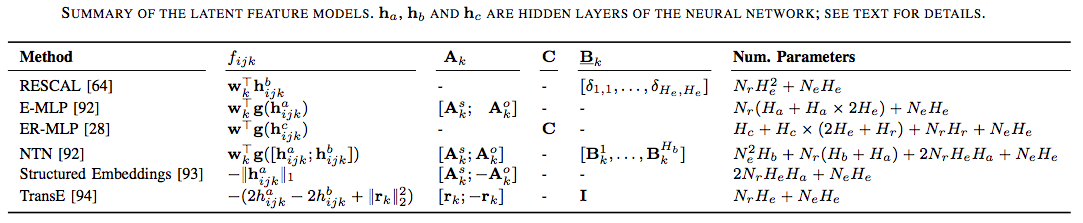
不同的方法可以归纳成为相同的框架,对比如下。
Following table summarizes the different models we have discussed. Clearly the best model will be dataset dependent.
Graph Feature Models
下面介绍基于图特征的模型(特征来自于图的结构:节点、边等)。
In graph feature models, we assume that the existence of an edge can be predicted by extracting features from the observed edges in the graph.
Similarity measures for uni-relational data
针对单一关系(有/无联系),可以采用图结构的相似度进行估计。
The intuition behind these methods is that similar entities are likely to be related (homophily) and that the similarity of entities can be derived from the neighborhood of nodes or from the existence of paths between nodes.
相似性包括:局部相似性(例如具有共同的邻居节点)、全局相似性(考虑节点间所有可达路径,例如PageRank)、类局部相似性(类似于全局相似性,但对可达路径的长度进行限制,为了减少计算量)。
- Local similarity indices such as Common Neighbors, the Adamic-Adar index or Preferential Attachment derive the similarity of entities from their number of common neighbors or their absolute number of neighbors. However, they can be too localized to capture important patterns in relational data and cannot model long-range or global dependencies.
- Global similarity indices such as the Katz index and the Leicht-Holme-Newman index derive the similarity of entities from the ensemble of all paths between entities, while indices like Hitting Time, Commute Time, and PageRank derive the similarity of entities from random walks on the graph.
- Quasi-local similarity indices like the Local Katz index or Local Random Walks try to balance predictive accuracy and computational complexity by deriving the similarity of entities from paths and random walks of bounded length.
Rule Mining and Inductive Logic Programming
规则和归纳方法的核心思路是,基于逻辑归纳的算法,推导出规则,再根据规则抽取出关系。
This method extracts rules via mining methods and uses these extracted rules to infer new links.
规则和归纳方法主要包括ALEPH和AMIE两种。
- ALEPH is an Inductive Logic Programming (ILP) system that attempts to learn rules from relational data via inverse entailment.
- AMIE is a rule mining system that extracts logical rules based on their support in a knowledge graph.
规则和归纳的方法的好处在于解释性强,但由于规则通常比较严苛,因此模式的覆盖面较窄。
Rule-based method is easily interpretable. However, rules over observed variables cover usually only a subset of patterns in knowledge graphs (or relational data) and useful rules can be challenging to learn.
Path Ranking Algorithm
路径排序的方法的核心思路是,基于随机游走的方法计算出各条可达路径的概率,并将其作为特征进行拟合。
We can compute the probability of following a path by assuming that at each step, we follow an outgoing link uniformly at random. The key idea in PRA is to use these path probabilities as features for predicting the probability of missing edges.
首先计算出可达路径的概率作为特征。
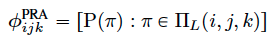
基于特征采用逻辑斯特回归等回归方法进行拟合。
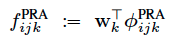
Combining latent and graph feature models
由于基于隐含特征和基于图特征的方法的假设不用,因此并不矛盾反而可以互补,因此可以结合两方面特征建立综合模型。
The strengths of latent and graph-based models are often complementary, as both families focus on different aspects of relational data:
隐含特征模型和图特征模型的优势对比如下。
- Latent feature models are well-suited for modeling global relational patterns via newly introduced latent variables. They are computationally efficient if triples can be explained with a small number of latent variables.
- Graph feature models are well-suited for modeling local and quasi-local graphs patterns. They are computationally efficient if triples can be explained from the neighborhood of entities or from short paths in the graph.
Additive relational effects model
为了结合两种模型,可采用加性模型,即针对两方面特征分别建立拟合项,以相加的方式进行拟合,表达式如下。
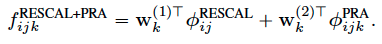
训练过程可以交替优化两个模型对应的拟合项。
ARE models can be trained by alternately optimizing the RESCAL parameters with the PRA parameters.
Other combined models
除了加性模型也可以采用其他模型进行结合,例如针对不同类关系分别建立拟合项进行拟合。
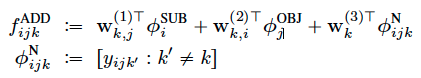
The term \Phi captures patterns efficiently where the existence of a triple y' is predictive of another triple y between the same pair of entities (but of a different relation type).
另一种思路是采用模型融合,首先分别针对两种模型进行训练,最终预测时结合多个模型的预测结果。
An alternative way to combine different prediction systems is to fit them separately, and use their outputs as inputs to another "fusion" system.
模型融合的好处在于灵活(可以任意增减子模型),缺点是子模型间缺乏协作,且子模型都较为复杂。
Stacking has the advantage that it is very flexible in the kinds of models that can be combined. However, it has the disadvantage that the individual models cannot cooperate, and thus any individual model needs to be more complex than in a combined model which is trained jointly.
相关连接
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.00759.pdf
- http://people.ee.duke.edu/~lcarin/Piyush06.12.2015.pdf