Clustering Uncertain Data
Clustering Uncertain Data
Clustering Uncertain Data
通常的聚类针对点(属性值)进行计算,而非针对不确定数据(Uncertain Data)或指数据在不同维度上的分布。
Clustering on uncertain data, one of the essential tasks in mining uncertain data, posts significant challenges on both modeling similarity between uncertain objects and developing efficient computational methods.
常用的聚类算法包括基于划分(partitioning)的方法(例如k-means)和基于密度(density-based)的方法(例如DBSCAN),其原理都是基于数据点之间的几何距离(geometric distances between objects)进行计算。常用的聚类算法不能针对不确定数据,因为几何中心相近的数据,其分布特性可能相差甚远。
The previous methods extend traditional partitioning clustering methods like k-means and density-based clustering methods like DBSCAN to uncertain data, thus rely on geometric distances between objects. Such methods cannot handle uncertain objects that are geometrically indistinguishable, such as products with the same mean but very different variances in customer ratings. Surprisingly, probability distributions, which are essential characteristics of uncertain objects, have not been considered in measuring similarity between uncertain objects.
论文提出了一种针对不确定数据的聚类算法。
Clustering Uncertain Data Based on Probability Distribution Similarity
https://www.computer.org/csdl/trans/tk/2013/04/ttk2013040751.pdf
主要内容包括两个方面:基于KL的相似度度量和聚类方法,基于核密度估计的快速算法。
- use the well known Kullback-Leibler divergence to measure similarity between uncertain objects in both the continuous and discrete cases, and integrate it into partitioning and density-based clustering methods to cluster uncertain objects.
- estimate KL divergence in the continuous case by kernel density estimation and employ the fast Gauss transform technique to further speed up the computation
通常,不确定数据可以表示成概率分布,因此不能直接基于数值计算相似度而要基于分布。
Generally, an uncertain data object can be represented by a probability distribution. One challenge in this clustering task is that we need to consider the similarity between cameras not only in terms of their score values, but also their score distributions.
Limitations of Existing Work
以下总结了已有的聚类算法的不足之处,均不能捕捉概率分布的差异(只能捕捉均值差异)。
As an object in a certain data set is a single point, the distribution regarding the object itself is not considered in traditional clustering algorithms. Thus, the studies that extended traditional algorithms to cluster uncertain data are limited to using geometric distance-based similarity measures, and cannot capture the difference between uncertain objects with different distributions.
Partitioning clustering approaches
This method extend the k-means method with the use of the expected distance to measure the similarity between two uncertain objects. As every object has the same center, the expected distance-based approaches cannot distinguish the two sets of objects having different distributions.
Density-based clustering approaches
The basic idea behind the algorithms does not change – objects in geometrically dense regions are grouped together as clusters and clusters are separated by sparse regions. However, in our case, objects heavily overlap. There is no clear sparse regions to separate objects into clusters. Therefore, the density-based approaches cannot work well.
Possible world approaches
A set of possible worlds are sampled from an uncertain data set. Each possible world consists of an instance from each object. Clustering is conducted individually on each possible world and the final clustering is obtained by aggregating the clustering results on all possible worlds into a single global clustering. The goal is to minimize the sum of the difference between the global clustering and the clustering of every possible world. The possible world approaches often cannot provide a stable and meaningful clustering result at the object level, not to mention that it is computationally infeasible due to the exponential number of possible worlds.
Kullback-Leibler divergence
为了计算两个分布之间的相似度或距离,可以采用KL散度(Kullback-Leibler divergence),在信息论中又称为相对熵(一个分布相对另一个分布差异越大,能够提供的信息量越大)。
In information theory, the similarity between two distributions can be measured by the Kullback-Leibler divergence (KL divergence for short, also known as information entropy or relative entropy).
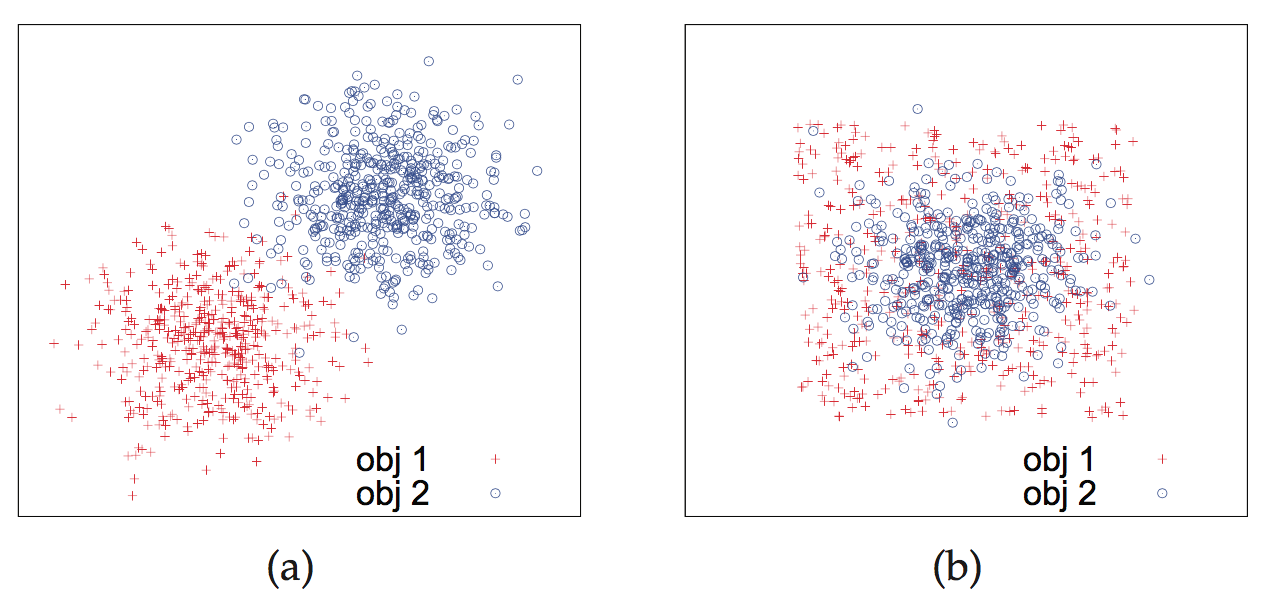
分布差异不能通过计算几何距离进行度量,如图,均值相近而分布各异的两个数据,不能通过计算几何距离进行区分,而需要计算分布的相似度(可采用KL散度)。
The distribution difference cannot be captured by geometric distances.The two objects (each one is represented by a set of sampled points) have different geometric locations. Their probability density functions over the entire data space are different and the difference can be captured by KL divergence. Although the geometric locations of the two objects are heavily overlapping, they have different distributions (one is uniform and the other is Gaussian). The difference between their distributions can also be discovered by KL divergence, but cannot be captured by the existing methods.
针对离散数据类型和连续数据类型,数据的分布可分别表示为离散随机变量(discrete random variable)及概率分布(probability distribution)或连续随机变量(continuous random variable)及概率密度分布(probability density function)。
If the domain is discrete (e.g., categorical) with a finite or countably infinite number of values, the object is a discrete random variable and its probability distribution is described by a probability mass function (pmf for short). Otherwise if the domain is continuous with a continuous range of values, the object is a continuous random variable and its probability distribution is described by a probability density function (pdf for short).
离散概率分布如下。
For discrete domains, the probability mass function of an uncertain object can be directly estimated by normalizing the number of observations against the size of the sample. Formally, the pmf of object P is
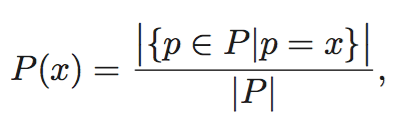
概率密度分布如下。
For continuous domains, we estimate the probabil- ity density function of an uncertain object by kernel density estimation. In 1-dimensional case, the density estimator is
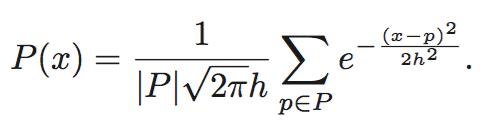
For the d-dimensional (d ≥ 2) case, the kernel function is the product of d Gaussian functions, each with its own bandwidth hj (1 ≤ j ≤ d), and the density estimator is
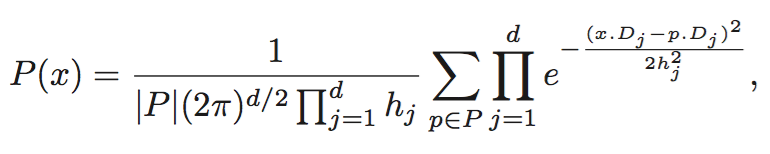
于此对应,KL散度在离散和连续数据的情况下可分别计算如下。
In general, KL divergence between two probability distributions is defined as follows,
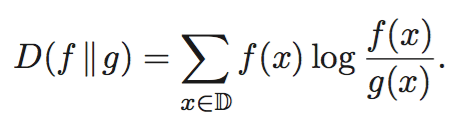
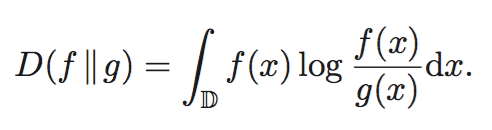
KL散度要求f(x)和g(x)均大于零(分母约束),且不符合对称性。
In both discrete and continuous cases, KL divergence is defined only in the case where for any x in domain D if f(x) > 0 then g(x) > 0. Note that, KL divergence is not symmetric in general, that is, D(f ∥g) ̸= D(g∥f).
Using KL Divergence as Similarity
KL散度非负,且符合吉布斯不等式,即KL散度越小,数据越相似。
KL divergence is always non-negative, and satisfies Gibbs’ inequality. That is, D(P ∥Q) ≥ 0 with equality only if P = Q. Therefore, the smaller the KL divergence, the more similar the two uncertain objects.
model every uncertain object to be clustered as a random variable in the same bounded domain D and represent it with a sample of i.i.d. observations.
Clustering Algorithms
Partitioning Clustering Methods
基于KL散度的相似度度量能够对数据进行聚类(基于划分或密度),目标是最小化一个类内部的KL散度。
Using KL divergence as similarity, a partitioning clustering method tries to partition objects into k clusters and chooses the best k representatives, one for each cluster, to minimize the total KL divergence as below,
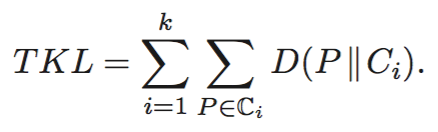
k-means和k-medoids是两种基于划分的聚类算法,差异在于一个计算均值,一个计算中值。
k-means and k-medoids are two classical partitioning methods. we adopt the k-medoids method to demonstrate the performance of partitioning clustering methods using KL divergence to cluster uncertain objects.
基于k-medoids的聚类算法包括下面两个步骤,即初始化和迭代优化。
- Building Phase: In the building phase, the uncertain k-medoids method obtains an initial clustering by selecting k representatives one after another.
- Swapping Phase: In the swapping phase, the uncertain k-medoids method iteratively improves the clustering by swapping a non-representative object with the representative to which it is assigned.
可以采用随机的方法进行优化。
The randomized k-medoids method, instead of finding the optimal non-representative object for swapping, randomly selects a non-representative object for swapping if the clustering quality can be improved. We follow the simulated annealing technique to prevent the method from being stuck at a local optimal result.
Density-Based Clustering Methods
基于密度的方法类似于DBSCAN, 依次找出密度稠密的区域。
The uncertain DBSCAN method finds dense regions through core objects whose ε-neighborhood contains at least μ objects.
具体计算过程解释如下。
Initially, every core object forms a cluster. Two clusters are merged together if a core object of one cluster is density-reachable from a core object of the other cluster. A non-core object is assigned to the closest core object if it is direct density reachable from this core object. The algorithm iteratively examines objects in the data set until no new object can be added to any cluster.
需要注意的是密度可达性是非对称的,但不是由于KL散度的计算引起的。
Note that direct density-reachability described above is an asymmetric relationship. This is not caused by the asymmetry of KL divergence.
Boosting Computation
为了优化计算,可以采用泰勒级数展开取前N项进行近似,原理在于计算核密度的时候距离中心较远的点贡献很小,但严格计算将引入很大的计算量,取泰勒级数相当于限定空间范围。
The main idea of approximating the sum of a series of Gaussian functions is to make use of the fact that the probability density of the Gaussian function decays exponentially and is negligible outside a certain distance to the center of the Gaussian. The fast Gauss transform is one of the best techniques to do the job. It reduces the computational complexity from O(N × M) to O(N + M) using a divide-and-conquer strategy and combined with the manipulation of Hermite polynomial expansions and Taylor series.
The improved fast Gauss transform takes advantages of the exponential decay of the Gaussian. Another key technique is to expand the sum of Gaussian functions into a multivariate Taylor expansion and truncate the series after degree p, where p is chosen to be sufficiently large such that the bounded error is no more than the precision parameter ε.
具体计算过程如下。
- Step 1:Approximate the sample of C by clustering.
- Step 2:Choose parameter p for truncating Taylor expansion.
- Step 3:Compute the coefficients of the Taylor expansion.
- Step 4:Compute the sum of approximated Gaussian functions.
相关连接
- https://www.computer.org/csdl/trans/tk/2013/04/ttk2013040751.pdf