Knowledge Graph
Knowledge Graph
Knowledge Graph
知识图谱,也称为科学知识图谱,它通过将应用数学、图形学、信息可视化技术、信息科学等学科的理论与方法与计量学引文分析、共现分析等方法结合,用可视化技术描述知识资源及其载体,挖掘、分析、构建、绘制和显示知识及它们之间的相互联系。为学科研究提供切实的、有价值的参考。
知识图谱的构建算法可以分为两大类:基于latent feature模型的方法和基于图模式挖掘的方法。
知识图谱的构建问题可以细化成Statistical Relational Learning的学习和预测问题,其描述如下。
In Statistical Relational Learning (SRL), the representation of an object can contain its relationships to other objects. Thus the data is in the form of a graph, consisting of nodes (entities) and labelled edges (relationships between entities). The main goals of SRL include prediction of missing edges, prediction of properties of nodes, and clustering nodes based on their connectivity patterns.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Statistical_relational_learning
Statistical Relational Learning (SRL)的子问题包括:
- collective classification, i.e. the (simultaneous) prediction of the class of several objects given objects' attributes and their relations
- link prediction, i.e. predicting whether or not two or more objects are related
- link-based clustering, i.e. the grouping of similar objects, where similarity is determined according to the links of an object, and the related task of collaborative filtering, i.e. the filtering for information that is relevant to an entity (where a piece of information is considered relevant to an entity if it is known to be relevant to a similar entity).
目前知识图谱的成功实现案例包括下列。
Recently, a large number of knowledge graphs have been created, including YAGO, DBpedia, NELL, Freebase, and the Google Knowledge Graph.
其限制和实现方法如下所示。
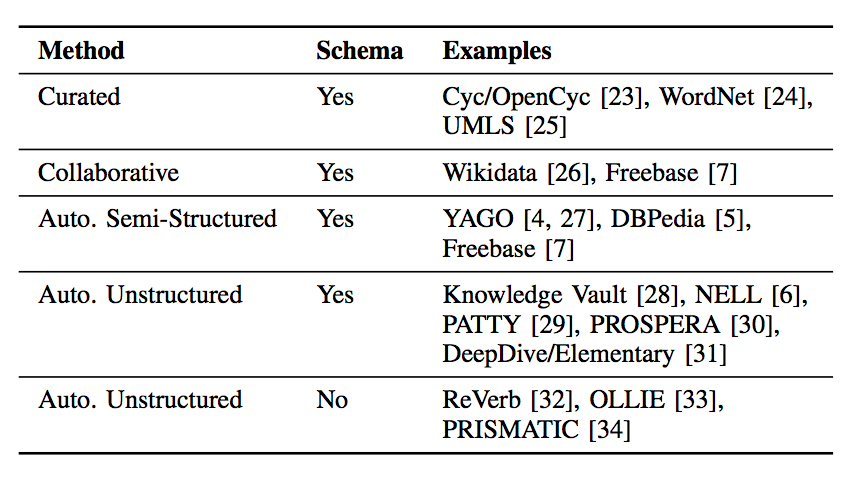
一个简单的知识图谱的例子如下,主要由结点(实体)和边(关系类别)构成。
Sample knowledge graph. Nodes represent entities, edge labels represent types of relations, edges represent existing relationships.
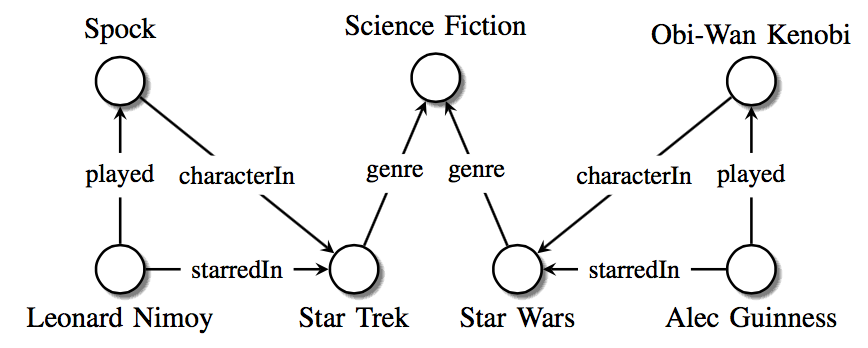
通常为了构建知识图谱,需要抽取二元关系,并将其表示成三元组的形式(subject, predicate, object)或称为SPO。
Represent facts in the form of binary relationships, in particular (subject, predicate, object) (SPO) triples, where subject and object are entities and predicate is the relation between them.
针对知识图谱示例,三元组如下。
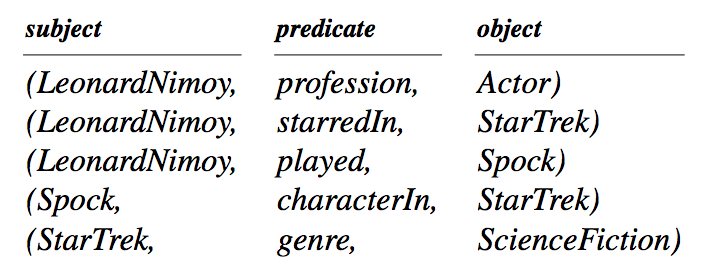
对三元组中的结点(实体)进行整合(连接)通常就能表示成知识图谱。
Combine all the SPO triples together to form a multi-graph, where nodes represent entities (all subjects and objects), and directed edges represent relationships.
针对知识图谱中不存在的边通常有两种假设。
- Under the closed world assumption (CWA), non-existing triples indicate false relationships.
- Under the open world assumption (OWA), a non-existing triple is interpreted as unknown, i.e., the corresponding relationship can be either true or false.
通常评价知识图谱的好坏或可用性的指标是:完整性、准确性和数据质量。
Completeness, accuracy, and data quality are important parameters that determine the usefulness of knowledge bases and are influenced by the way knowledge bases are constructed.
知识图谱的构建通常可以粗分为下面4中方法。
Knowledge base construction methods:
- In curated approaches, triples are created manually by a closed group of experts.
- In collaborative approaches, triples are created manually by an open group of volunteers.
- In automated semi-structured approaches, triples are extracted automatically from semi-structured text (e.g., infoboxes in Wikipedia) via hand-crafted rules, learned rules, or regular expressions.
- In automated unstructured approaches, triples are extracted automatically from unstructured text via machine learning and natural language processing techniques.
下面主要简单介绍基于机器学习的两种方法,具体的算法将在后续文章中展开。
LATENT FEATURE MODELS
隐含特征模型的方法捕捉了结点间的隐含关系。
Latent feature models capture the correlation between the nodes/edges using latent variables. The key intuition behind relational latent feature models is that the relationships between entities can be derived from interactions of their latent features.
RESCAL: A bilinear model
RESCAL是一种典型的隐含特征模型,通过特征抽取计算实体间关联,并通过矩阵或张量分解,对主成分数量进行约束,捕捉隐含特征,从而对未知关系(边)进行填充(识别)。
RESCAL is a relational latent feature model which explains triples via pairwise interactions of latent features.
其数学表示如下。
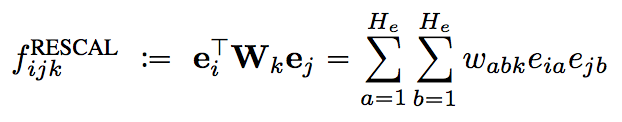
where Wk is a weight matrix whose entries wabk specify how much the latent features a and b interact in the k-th relation. It is called a bilinear model, since it captures the interactions between the two entity vectors using multiplicative terms.
张量分解的过程如下所示。
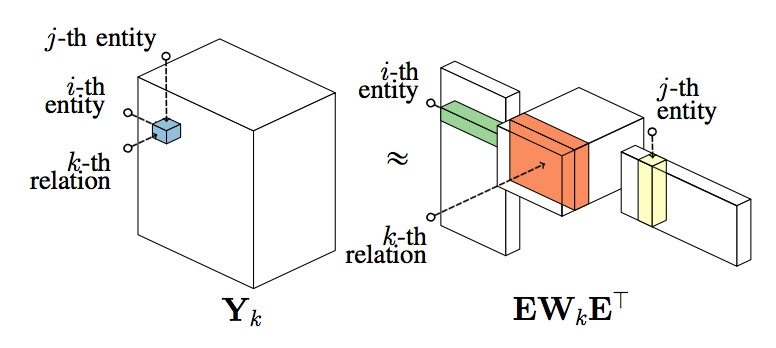
张量分解也可以表示如下的神经元网络形式,输入层、隐含层、输出层全连接对应了矩阵乘法,隐含层结点对应了核张量,因此可以采用神经元网络的训练方法优化模型参数。
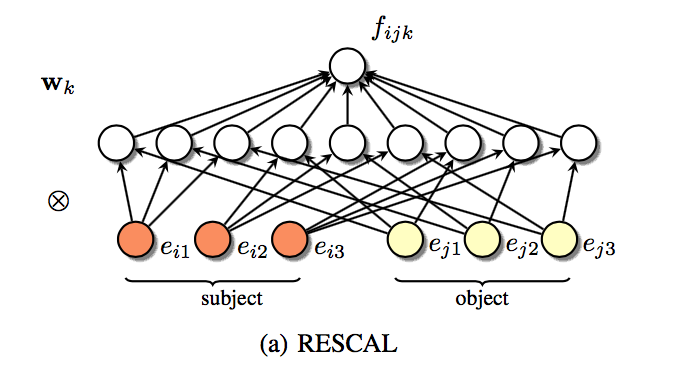
Since all parameters are learned jointly, these shared representations permit to propagate information between triples via the latent representations of entities and the weights of relations. This allows the model to capture global dependencies in the data.
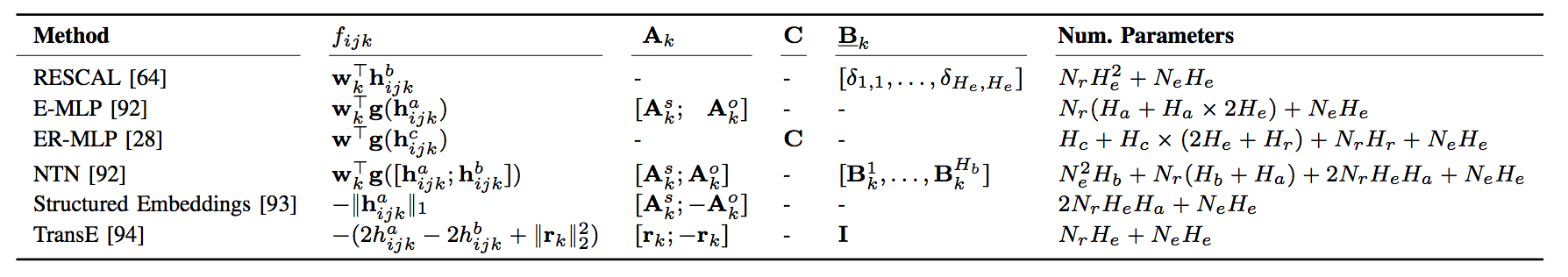
隐含特征模型的其他方法如下。
- Other tensor factorization models
- Matrix factorization methods
- Multi-layer perceptrons
- Neural tensor networks
- Latent distance models
GRAPH FEATURE MODELS
不同于隐含特征模型,图特征模型直接对于图中结点连接关系的模式进行学习。通过对包含已知相关结点的局部网络模型进行外推,对未知边进行识别。
Graph feature models capture the correlation directly using statistical models based on the observable properties of the graph. In graph feature models, it is assumed that the existence of an edge can be predicted by extracting features from the observed edges in the graph.
图特征模型方法可以细分成下面3中方法。
Similarity measures for uni-relational data
The intuition behind these methods is that similar entities are likely to be related (homophily) and that the similarity of entities can be derived from the neighborhood of nodes or from the existence of paths between nodes. For this purpose, various indices have been proposed to measure the similarity of entities, which can be classified into local, global, and quasi-local approaches.Rule Mining and Inductive Logic Programming
Another class of models that works on the observed variables of a knowledge graph extracts rules via mining methods and uses these extracted rules to infer new links. The extracted rules can also be used as a basis for Markov Logic.Path Ranking Algorithm The Path Ranking Algorithm (PRA) extends the idea of using random walks of bounded lengths for predicting links in multi-relational knowledge graphs.
后续文章将详细分析上面提到的主要算法。
相关连接
- https://arxiv.org/pdf/1503.00759.pdf
- http://people.ee.duke.edu/~lcarin/Piyush06.12.2015.pdf