SyntaxNet原理分析(2)
SyntaxNet原理分析(2)
SyntaxNet原理分析(2)
SyntaxNet作为一个parser(NLP系统中的关键组件之一),能够针对系统中输入一个句子,自动给句子中的每一个单词打上POS(part-of-Speech)标签,用来描述这些词的句法功能,之后在依存句法树中呈现。这些句法关系直接涉及句子的潜在含义。
SyntaxNet基于arc-standard system(one of the most popular transition systems)实现。arc-standard system的介绍可参考:SyntaxNet原理分析(1)。
http://qiangsiwei.github.io/blog/notes/2016/05/18/SyntaxNet.html
在arc-standard system中,一个configuration c = (s,b,A)由一个栈区(stack s),一个缓冲区(buffer b),和一组依存弧(dependency arcs A)组成。初始状态下,栈区仅包含根结点ROOT,依存弧为空,文本全部处于缓冲区。随着文本不断从左至右读入,arc-standard system可以进行以下三种操作,并最终清空缓冲区,并合并栈区中的结点(仅存ROOT结点),由依存弧组成树形结构,构成依存树。
SyntaxNet主要由两部分组成,特征抽取过程和基于神经元网络的parsing过程。如下图所示,左侧主要用于特征抽取(Sparse feature extraction),特征抽取基于transition system,输出stack和buffer内的状态(word、POS label、arc label)以及标注的transition label。神经元网络首先对特征进行连接,然后经过隐含层、激发层、输出层等深层结构进行计算和优化。特征抽取的实现基于C++,神经元网络的实现基于TensorFlow,特征抽取和神经元输入之间的数据传递通过protobuf(Google's data interchange format)。
https://github.com/google/protobuf
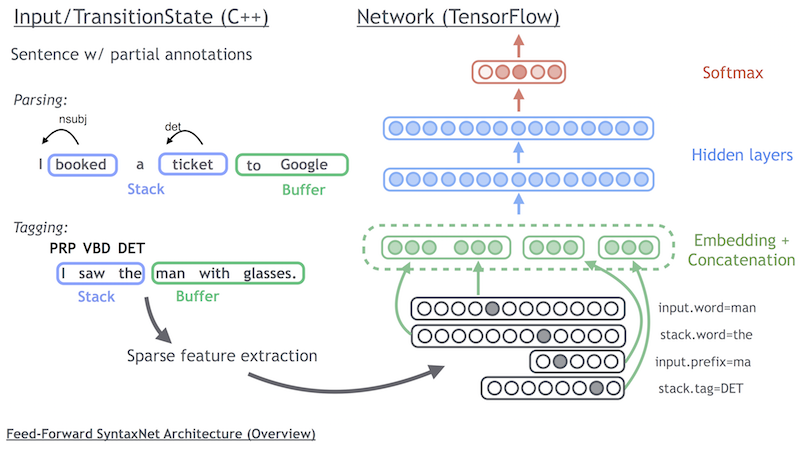
基于transition system,提供以下三种状态转换操作。
SHIFT: Push another word onto the top of the stack, i.e. shifting one token from the buffer to the stack.
LEFT_ARC: Pop the top two words from the stack. Attach the second to the first, creating an arc pointing to the left. Push the first word back on the stack.
RIGHT_ARC: Pop the top two words from the stack. Attach the second to the first, creating an arc point to the right. Push the second word back on the stack.
依存树的构造问题可以转化成在当前configuration下,transition的预测问题,问题描述如下。

SyntaxNet在Github上提供了如下很好的动图说明了对"I booked a ticket to Google"这句话的解析(状态转移)全过程。
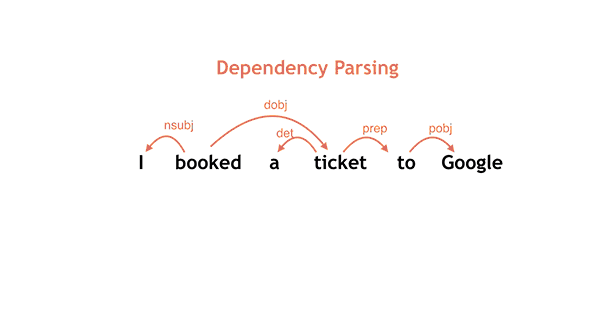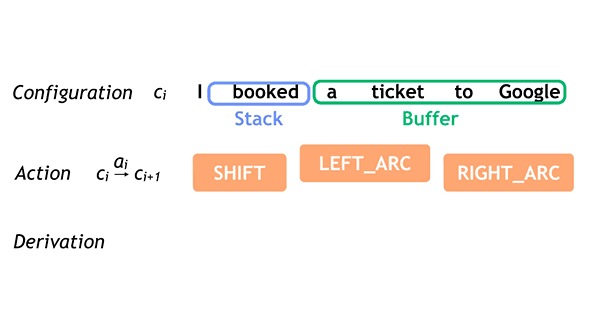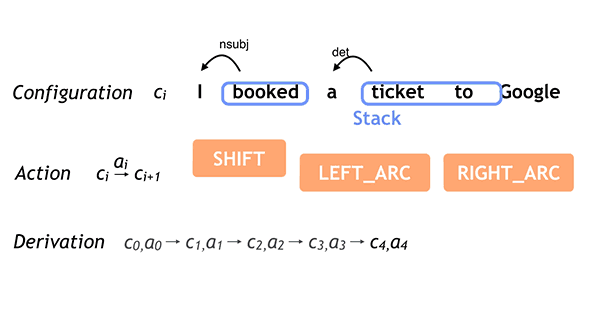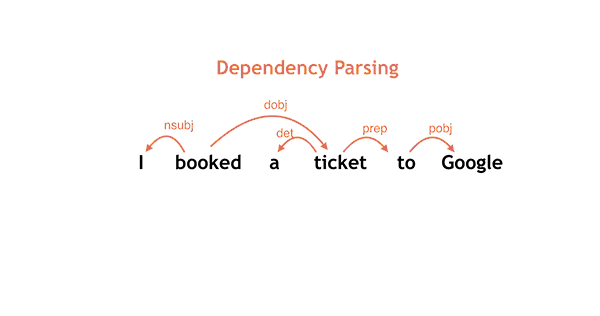
计算机正确处理句法分析困难的最大原因是语言的歧义性。
通常一个中等长度的句子会具有数百、数千甚至数万种可能的句法结构,为了做出正确的解析,句法分析器必须能够搜索所有这些结构选择,并找到给定语境下最合理的那个结构。
长句中的多重歧义会共同造成句子的可能结构数量的组合爆炸,而这些结构中的绝大多数都极其不合理(但仍然是可能的),句法分析器必须以某种方式来丢弃它们。
SyntaxNet将神经网络运用于歧义问题。
为了扩大搜索区域(不局限与基于贪心法的当前步最优),又对搜索空间进行限制(不至于为了达到全局最优付出指数增长计算量的代价),SyntaxNet使用了Beam Search(集束搜索)算法进行优化。
Beam Search不是直接取每步的最优决定,而是在每步都保留多个部分性假设,只有当存在多个得分更高的假设的时候,一个假设才会被抛弃。
Beam Search的原理如下图所示。
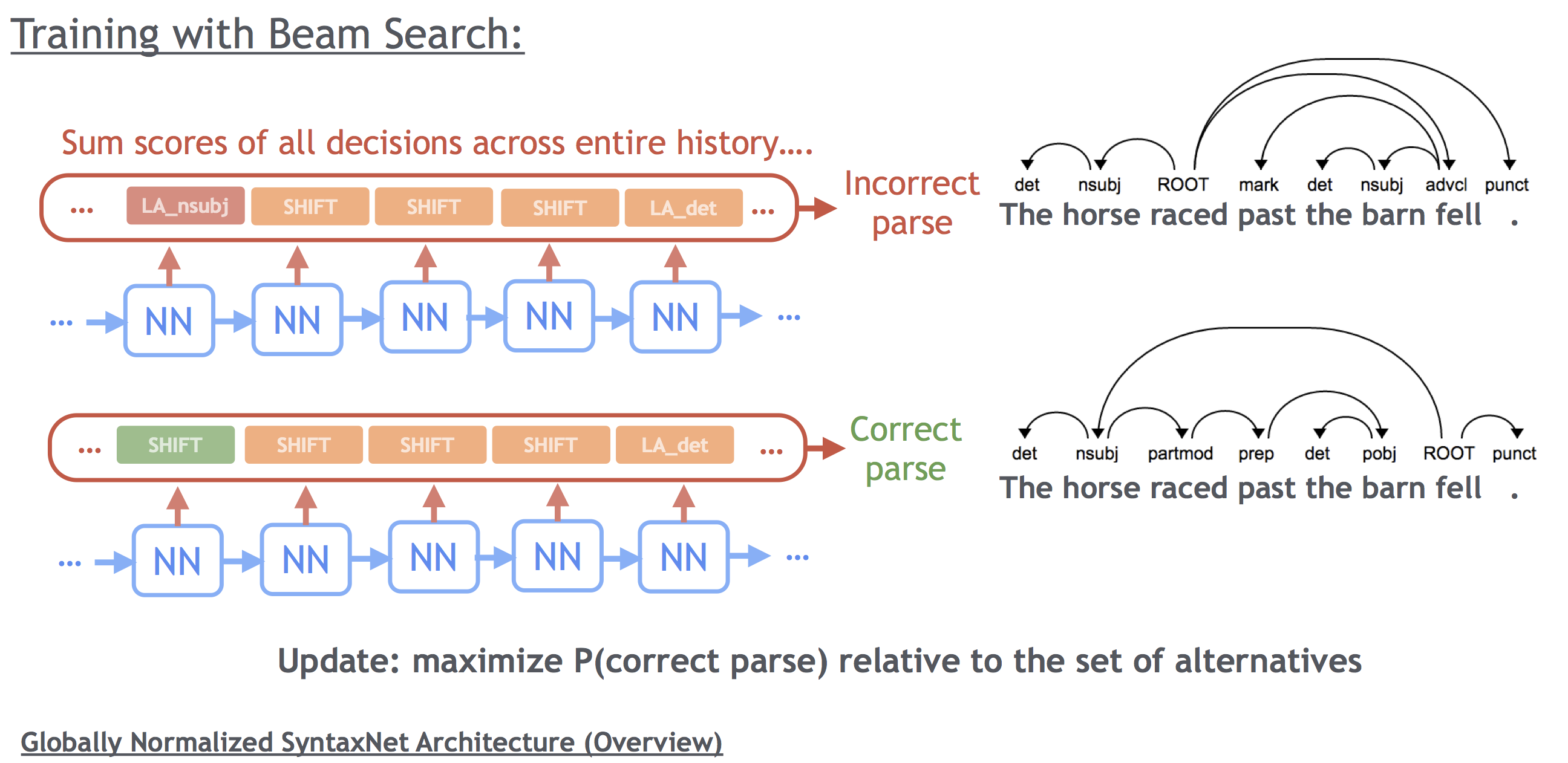
SyntaxNet算法可以参考论文"Globally Normalized Transition-Based Neural Networks"。
http://arxiv.org/pdf/1603.06042v1.pdf
transition预测问题中每一种决策(decision or dj)的概率计算如下。其中Z是归一化子式。
针对局部(local)的优化,Z是当前状态下(有前j-1步决策d1:j-1唯一确定)所有可能的决策的概率之和。
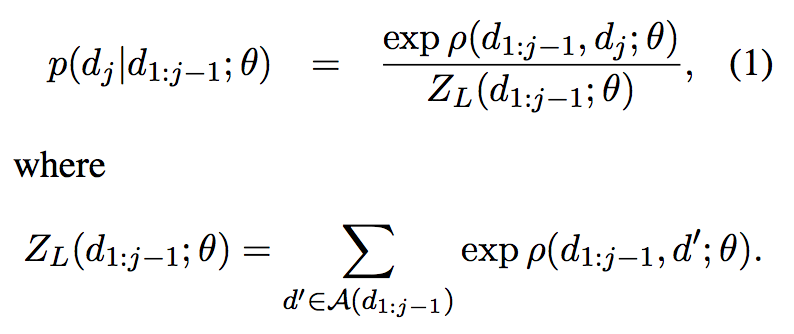
那么到第j步决策完成时,似然(Likelihood)为之前每步概率的乘积,如下式。
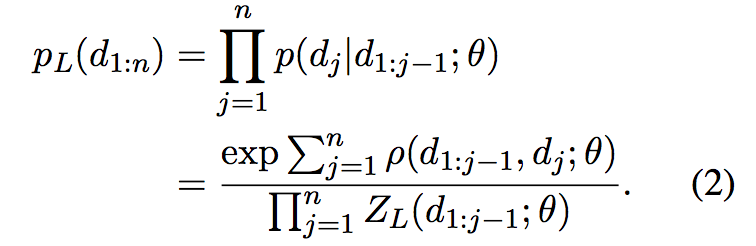
为了扩大搜索区域(解决歧义问题),达到全局最优(考虑所有状态的累计),决策概率和归一化Z如下。
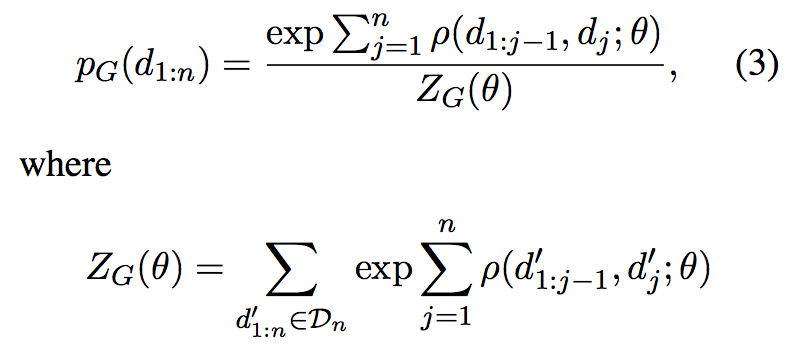
基于全局优化的优化目标如下,并由此可见该问题的求解可以采用Beam Search进行优化(Beam search can again be used to approximately find the argmax)。
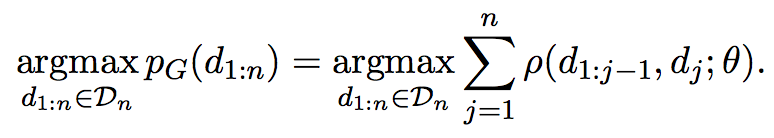
下面两式分别是基于局部优化和全局优化的负对数似然,并可采用随机梯度下降进行求解(stochastic gradient descent on the negative log-likelihood of the data under the model)。
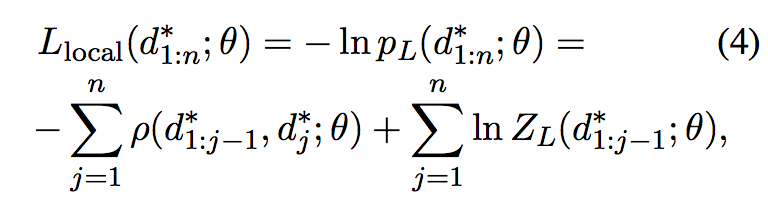
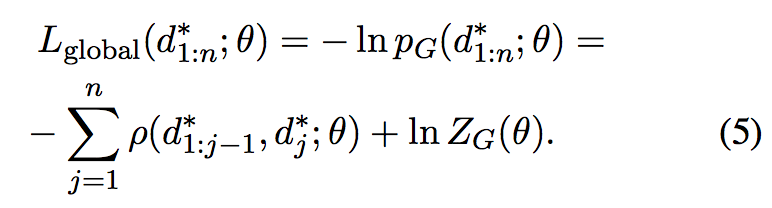
并由此可见基于局部优化的好处在于可以对目标函数进行分解后逐个进行优化,而基于全局的优化则无法进行分解。A significant practical advantange of the locally normalized cost is that it factorizes into n independent terms, each of which can be computed exactly and minimized separately. By contrast, the ZG term is in many cases intractable.
为了进行全局优化,SyntaxNet采用了beam search和early updates方法(To make learning tractable with the globally normalized model, we use beam search and early updates)。
Beam Search的原理是在每步都保留多个部分性假设,只有当存在多个得分更高的假设的时候,一个假设才会被抛弃。As the training sequence is being decoded, we keep track of the location of the gold path in the beam. If the gold path falls out of the beam at step j, a stochastic gradient step is taken on the following objective.
Beam Search的优化目标如下。
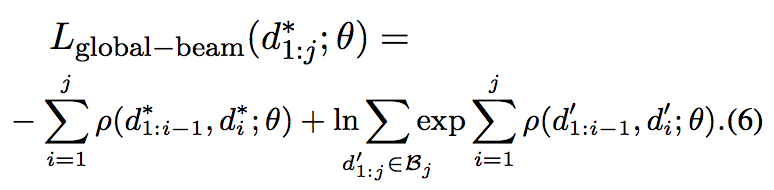
Beam Search和Early Updates算法可以参考论文"Incremental parsing with the perceptron algorithm"。
http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/P04-1015
相关连接
- https://github.com/qiangsiwei/models/tree/master/syntaxnet