LFG-Based Generation
LFG-Based Generation
LFG-Based Generation
句子生成(或称为表层实现)是指从给定的抽象语义逻辑生成符合句法、词形、拼写的句子。常用的句法解析或生成方法包括:Lexical Functional Grammar (LFG), Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar (HPSG), Combinatory Categorial Grammar (CCG), Tree Adjoining Grammar (TAG)等。
各种方法的详细内容可参考ACL讲座的ppt。本文主要介绍词汇功能语法(Lexical Functional Grammar (LFG))。
http://nlp.cs.illinois.edu/HockenmaierGroup/ACL2010Tutorial/ACL2010TutorialGrammars.pdf
Sentence generation, or surface realisation can be described as the problem of producing syntactically, morphologically, and orthographically correct sentences from a given abstract semantic / logical representation according to some linguistic theory, e.g. Lexical Functional Grammar (LFG), Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar (HPSG), Combinatory Categorial Grammar (CCG), Tree Adjoining Grammar (TAG) etc.
语法的解释如下,语法规则通常通过人工进行归纳总结,例如:LinGo、OpenCCG、XLE等。
Grammars, such as these, are declarative formulations of the correspondences between semantic and syntactic representations. Grammar rules have been carefully handcrafted, such as those used in LinGo (Carroll et al., 1999), OpenCCG (White, 2004) and XLE (Crouch et al., 2007).
人工归纳总结语法耗时费力,且与语言和领域相关(language-dependent and domain-specific),理想情况下语法能够通过带标注数据集进行自动生成。
As handcrafting grammar rules is time-consuming, language-dependent and domain-specific, recent years have witnessed research on extracting wide-coverage grammars automatically from annotated corpora, for both parsing and generation.
除了语法的自动生成,最近的研究还关注句子生成(表层实现)的自动化,所采用的方法主要基于generate-and-select paradigm。
In addition to applying statistical techniques to automatically acquire generation grammars, over the last decade, there has been a lot of interest in a generate-and-select paradigm for surface realisation.
这种方法首先生成一系列可能的形式,然后基于概率模型选择出其中最可能的一个。
The paradigm is characterised by a separation between generation and selection, in which symbolic or rule-based methods are used to generate a space of possible paraphrases, and statistical methods are used to select one or more outputs from the space.
针对context-free grammars (CFG)的研究通常范围两个方面:解析(parsing)和生成(generation)。主流研究聚焦在前者。
It is interesting to note that, while the study of how the granularity of context-free grammars (CFG) affects the performance of a parser (e.g. in the form of grammar transforms (Johnson, 1998) and lexicalisation (Collins, 1997)) has attracted substantial attention, to our knowledge, there has been a lot less research on this subject for surface realisation, a process that is generally regarded as the reverse process of parsing.
Lexical Functional Grammar
词汇功能语法(Lexical Functional Grammar)是一种形式语法,是美国计算语言学家布列斯南(Bresnan, J.)和卡普兰(Kaplan, R.)提出的一种用于自然语言处理的形式语法。
词汇功能语法对于一种语言的描写由短语结构规则和说明短语句法功能的功能方程两部分组成。它对于一个句子的描写由成分结构和功能结构组成。成分结构相当于一个语法树,树上的结点用短语标记来标注。功能结构相当于一个复杂特征集。功能结构由功能方程生成,用于描写句法树上每个结点的语法功能和谓词变元关系。词汇功能语法重视词汇信息的描述,整个语法由词汇来驱动。
关于词汇功能语法的详细说明可以参考如下。
http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjxx-xsb200819061
Lexical Functional Grammar (Kaplan and Bresnan, 1982) is a constraint-based grammar formalism which postulates (minimally) two levels of representation: c(onstituent)-structure and f(unctional)-structure.
词汇功能语法主要包括C-structure和F-structure两种模式,分别从不同的角度对句子进行描述。
C-structure takes the form of phrase structure trees and captures surface grammatical configurations. F-structure encodes more abstract grammatical functions (GFs) such as SUBJ(ect), OBJ(ect), ADJUNCT and TOPIC etc., in the form of hierarchical attribute-value matrices.
C-structure和F-structure可以相互对应。
C-structures and f-structures are related by a piecewise correspondence function φ that goes from the nodes of a c-structure tree into units of f-structure spaces (Kaplan, 1995).
C-structure和F-structure的一个例子如下。
C- and f-structures with φ links for the sentence "江泽民会见泰国总理"
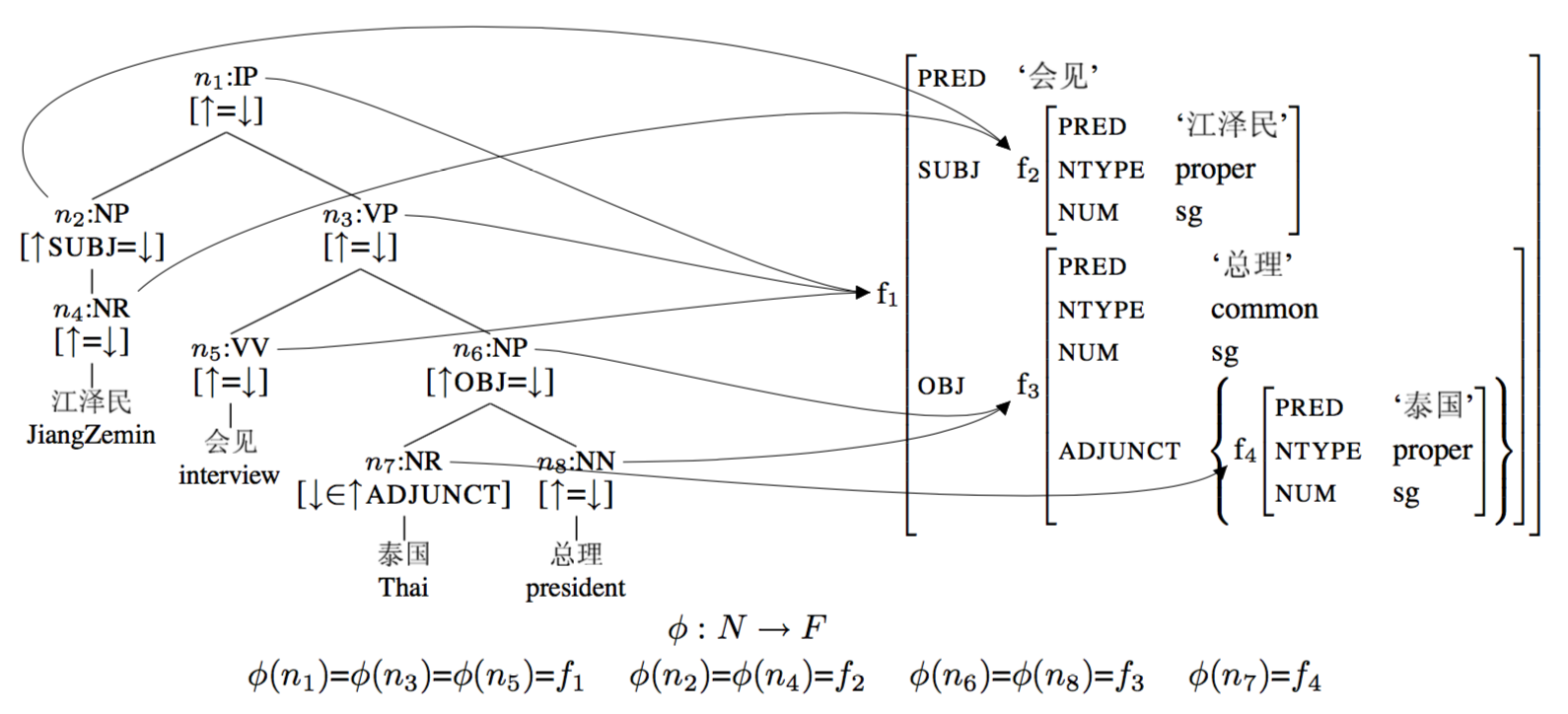
上例中采用的语法子集如下。
(1) shows a miniature set of annotated CFG rules (lexical entries omitted) which generates the c- and f-structure.

C-structure和F-structure中一些标号的解释如下。
In the functional annotations, (↓) refers to the f-structure associated with the local c-structure node ni, i.e. φ(ni), and (↑) refers to the f-structure associated with the mother (M) node of ni, i.e. φ(M(ni)).
Generation from f-Structures
基于LFG的生成模型的概率可以描述为P(T|F),其中T和F分别对应于C-structure和F-structure。
The LFG-based statistical generation model defines the conditional probability P(T|F), for each candidate functionally annotated c-structure tree T (which fully specifies a surface realisation) given an f-structure F.
P(T|F)可以进一步分解成为不同重写语法规则(X → Y)的概率的乘积。
P(T|F) is then decomposed as the product of the probabilities of all the functionally annotated CFG rewriting rules X → Y (conditioned on the left hand side (LHS) X and local features of the corresponding f-structure φ(X)) contributing to the tree T (Eq. 2).
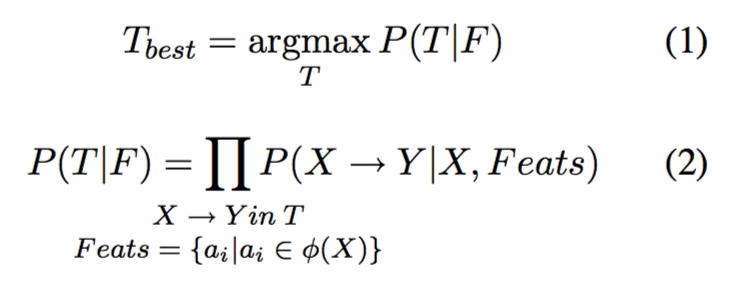
Disambiguation Models
常用的生成模型采用probabilistic context-free grammars,然而其中的独立性假设可能并不合适(一个句子中不同成分可能并非相互独立,而可能遵循一定的联合概率分布)。
The basic generation model presented in (Cahill and van Genabith, 2006) used simple probabilistic context-free grammars. However, the independence assumptions implicit in PCFG models may not be appropriate to best capture natural language phenomena.
A History-Based Model
基于历史的方法通过增加父节点对应的f-structure中的语法功能GF来弱化独立性假设。
The history-based (HB) approach which incorporates more context information has worked well in parsing (Collins, 1997; Charniak, 2000).
The history-based model increases the context by simply including the parent grammatical function GF of the f-structure in addition to the local φ-linked feature set in the conditioning context (Eq. 3).
数学描述如下。
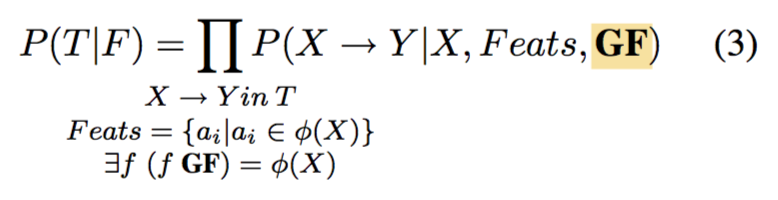
Though Chinese does not distinguish cases, the f-structure parent GF are expected to help predict grammar rule expansions more accurately in the tree derivation than the simple PCFG model.
A Lexicalised Model
词汇化语法规则通过包含更多的类型信息(可以理解为根据词义的分类)来弱化独立性假设。
Compared to the HB model which includes the parent grammatical function in the conditioning context, lexicalised grammar rules contain more fine-grained categorial information.
The expectation is that a lexicalised PCFG model also works better than a simple PCFG model in Chinese generation, considering e.g. prepositional phrase (PP) modification in Chinese.
一个例子如下,"往"可以位于谓词两边,但"对"一般只能位于谓词之前。

In order to model phenomena such as these, we head-lexicalise our grammar by associating each non-terminal node with the head word2 in the c-structure tree along the head-projection line.
由于数据稀疏性,可采用多模型融合进行数据平滑。
To handle the problem of sparse data while estimating rule probabilities, a back-off to baseline model is employed. As, from a linguistic perspective, it is the modifier rather than the head word which plays the main role in determining word order, a back-off to partial lexicalisation on the modifier only is also used for binary rules.
数学描述如下。
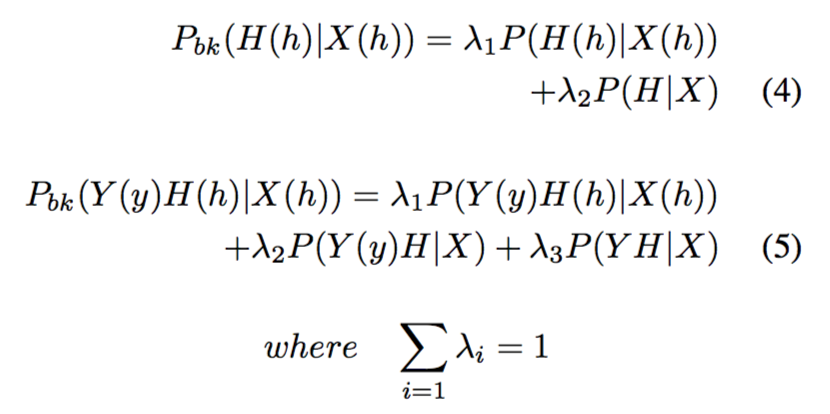
Chart Generation
基于PCFG的生成算法采用chart generator算法,从底至上依次生成最可能的子结构。
The PCFG-based generation algorithms are implemented in terms of a chart generator (Kay, 1996). In the generation algorithm, each (sub-)f-structure indexes a (sub-)chart. Each local chart generates the most probable trees for the local f-structure in a bottom-up manner:
算法的具体步骤如下。
- generating lexical edges from the the local GF PRED and some atomic features representing function words, mood or aspect etc.
- applying unary rules and binary rules to generate new edges until no any new edges can be generated in the current local chart.
- propagating compatible edges to the upper-level chart.
相关连接
- http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/W08-1112